High bilirubin in the blood: the main causes of an increase in newborns and adults, symptoms of high bilirubin, diet with elevated bilirubin
In the process of hemolysis, one of the end products of the decay of red blood cells is hemoglobin, which, going beyond the erythrocyte membranes, is transformed into a pigment that has a yellowish-brown color - unbound (indirect) bilirubin. This substance has extremely toxic properties and can accumulate in various tissues, gradually poisoning the body. This explains the concern of specialists when the results of a laboratory examination reveal a high in an adult or a child.
What it is
Indirect bilirubin after hemolysis processes is contained in the bloodstream and bile. Its excretion from the body occurs due to the conversion by liver cells into a bound form (direct bilirubin), which is excreted outside the body along with feces.
If the processes of transformation of bilirubin forms are disturbed, its concentration in the blood begins to increase, which leads to the penetration of the pigment into various tissues. Visually, this can be determined by the characteristic yellowish coloration of the skin and visible mucous membranes.
Norm
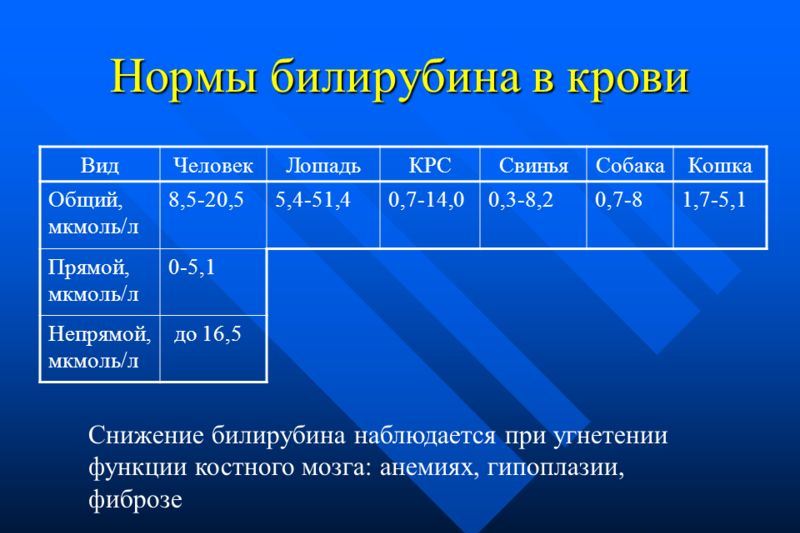
Determining the level of bilirubin is possible through a biochemical analysis. is a constant for all age categories of the population and does not depend on the gender of a person. Newborn babies are the only exception.
The norms of bilirubin in the blood are as follows:
- - 8.5 - 20 µmol / liter;
- direct bilirubin - up to 4.3 µmol / liter;
- indirect bilirubin - up to 15.4 µmol / liter.
Since immediately after birth, maternal blood also circulates in the vascular bed of the newborn, enhanced processes of red blood cells received from the mother are observed in the circulatory system of the child. This leads to the accumulation of indirect bilirubin in the blood, which explains the occurrence of physiological jaundice in children in the first weeks of life.
This process, subject to the normal course of hemolytic processes, does not pose a danger to the health of the baby, since by the beginning of the fourth week, the pigment concentration in his blood returns to normal:
- immediately after birth - 50 - 60 µmol / liter;
- the first week of life - an increase in the concentration of total bilirubin up to 250 µmol / liter;
- the second week of life - 90 µmol / liter;
- the third week of life - the content of total bilirubin becomes the same as in adults.
Raise
A condition in which there is an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is called hyperbilirubinemia. The reasons for the development of hyperbilirubinemia depend on the level of content of which form of pigment increases.
The concentration of indirect bilirubin increases with an increase in hemolytic processes and a violation of the transformation of this type of pigment into a bound form.
This happens in the following cases:
- Progression (congenital or acquired). At the same time, there are no other deviations in the body, and the growth of indicators of the indirect form of the pigment is associated with its accelerated formation.
- Damage to liver cells as a result of the progression of diseases of various etiologies, the target of which is this particular organ (hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors, and others). In this case, the transformation of the pigment is disturbed, and it goes beyond the liver in its original form.
Cumulation of the direct form of bilirubin is possible in the following clinical cases:
- Pathological processes of various etiologies, which are accompanied by a violation of the evacuation of bile outside the gallbladder. A similar complication develops with tumors of the digestive system, pancreatitis, cholelithiasis.
- Defeat by helminths.
- Side effects of certain drugs.
- Alcoholic or chemical intoxication.
- Development of neonatal jaundice.
- In pregnant women, the concentration of conjugated bilirubin occurs in the last weeks of pregnancy against the background of the development of hepatic cholestasis of pregnant women, due to changes in the hormonal background.
- which is quite common in teenagers.
Symptoms
The development of a pathological disorder in the body manifests itself in people in different ways and depends on the form of bilirubin that accumulates in the bloodstream.
However, the common symptoms of high bilirubin are as follows:
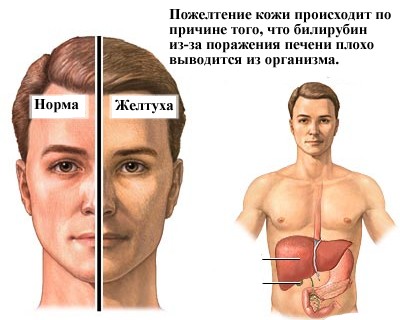
- change in the color of the skin and visible mucous membranes (they become yellowish);
- urine the color of beer;
- discoloration of feces;
- high body temperature;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, the presence of bitter belching;
In case of violation of the evacuation of bile, for example, as a result of blockage of the lumen of the bile duct by a stone or tumor, the following symptoms are added to the described symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- indigestion, diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- vomit;
- bouts of hepatic colic.
Treatment
With laboratory detection of high bilirubin, it is imperative to undergo an additional examination to establish the true cause of such a violation.
The tactics of therapeutic measures should be developed only by a qualified specialist, based on the results of a complete diagnosis. In questions of how to treat a change in biochemical parameters, they rely on its root cause.
Drug therapy is based on the use of the following pharmacological forms:
- drugs that have a choleretic effect;
- enzymes;
- medicines with hepatoprotective properties.
The choice, dose and regimen of taking any drug in this case is carried out only by the attending physician. Throughout the course of treatment, the specialist constantly monitors the dynamics of the course of the pathological process, correcting the treatment tactics if necessary.
In the absence of a positive result of conservative methods of treatment, urgent surgery may be required to eliminate blockage of the bile duct.
Nutrition
To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect when taking specific drugs, it is necessary to make certain changes in the usual diet with elevated bilirubin.
- daily there are various cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal). The exception is millet porridge;
- exclude excessively fatty, spicy, spicy dishes, marinades, black bread;
- when choosing a method of heat treatment of food, preference should be given to steam cooking;
- limit salt and protein intake;
- increase the amount of fluid consumed, from drinks it is better to choose compotes, fruit drinks. The use of coffee, tea should be limited as much as possible;
- exclude alcohol intake.
Folk remedies
From folk remedies for correcting the level of bilirubin in the blood, it is possible, after prior agreement with the attending physician, to use decoctions of chamomile, corn stigmas, St. John's wort, mint.
In no case should changes in the biochemical parameters of the blood be left, since the toxic effect of the pigment leads to severe damage to all body systems, primarily the nervous one.
